Extracting features from SONATA Network simulations¶
This notebook shows how to extract features of a group of cells from a SONATA network, specifically focusing on a small portion of non-barrel primary somatosensory cortex circuit from juvenile rats, with the help of BlueCellulLab. For those interested in conducting a more in-depth analysis, the entire circuit dataset is accessible on Zenodo. For more details about the simulation and in-depth insights on the circuit, please refer to the Bluecellulab SONATA Network example and the related paper, respectively.
Note: The compiled mechanisms need to be provided before importing bluecellulab.
!nrnivmodl ./mechanisms
import json
from pathlib import Path
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from bluecellulab import CircuitSimulation
import efel
In this example, a small sub-circuit has been extracted from the sscx circuit. This sub-circuit specifically consists of a random selection of cells exhibiting delayed stuttering (dSTUT) etype.
The simulation_config specifies the types of input stimuli to be applied to the cells. In this case, we have selected a ‘relative_linear’ stimulus of 70 ms and set the stimulus current at a level equivalent to 100 percent of the cell’s threshold current.
simulation_config = Path("./") / "simulation_config.json"
with open(simulation_config) as f:
simulation_config_dict = json.load(f)
print(json.dumps(simulation_config_dict, indent=4))
{
"manifest": {
"$OUTPUT_DIR": "."
},
"run": {
"tstop": 100.0,
"dt": 0.025,
"random_seed": 1
},
"conditions": {
"v_init": -65
},
"target_simulator": "NEURON",
"network": "./O1/circuit_config.json",
"node_set": "dSTUT_mini",
"output": {
"output_dir": "$OUTPUT_DIR/output_sonata",
"spikes_file": "out.h5",
"spikes_sort_order": "by_time"
},
"inputs": {
"continuous_linear": {
"input_type": "current_clamp",
"module": "relative_linear",
"delay": 20.0,
"duration": 70.0,
"percent_start": 100,
"node_set": "dSTUT_mini"
}
},
"reports": {
"soma": {
"cells": "dSTUT_mini",
"variable_name": "v",
"type": "compartment",
"dt": 1.0,
"start_time": 0.0,
"end_time": 20.0,
"sections": "soma",
"compartments": "center"
}
}
}
We use BlueCellulab for simulating smaller scale circuits, in contrast to the larger-scale simulations conducted with Neurodamus.
simulation_config = Path("./") / "simulation_config.json"
with open(simulation_config) as f:
simulation_config_dict = json.load(f)
sim = CircuitSimulation(simulation_config)
from bluepysnap import Simulation as snap_sim
snap_access = snap_sim(simulation_config)
import pandas as pd
from bluepysnap import Simulation as snap_sim
all_nodes = pd.concat([x[1] for x in snap_access.circuit.nodes.get()])
dstut_cells = all_nodes[all_nodes["etype"] == "dSTUT"].index.to_list()
sim.instantiate_gids(dstut_cells, add_stimuli=True)
t_stop = 100.0
sim.run(t_stop)
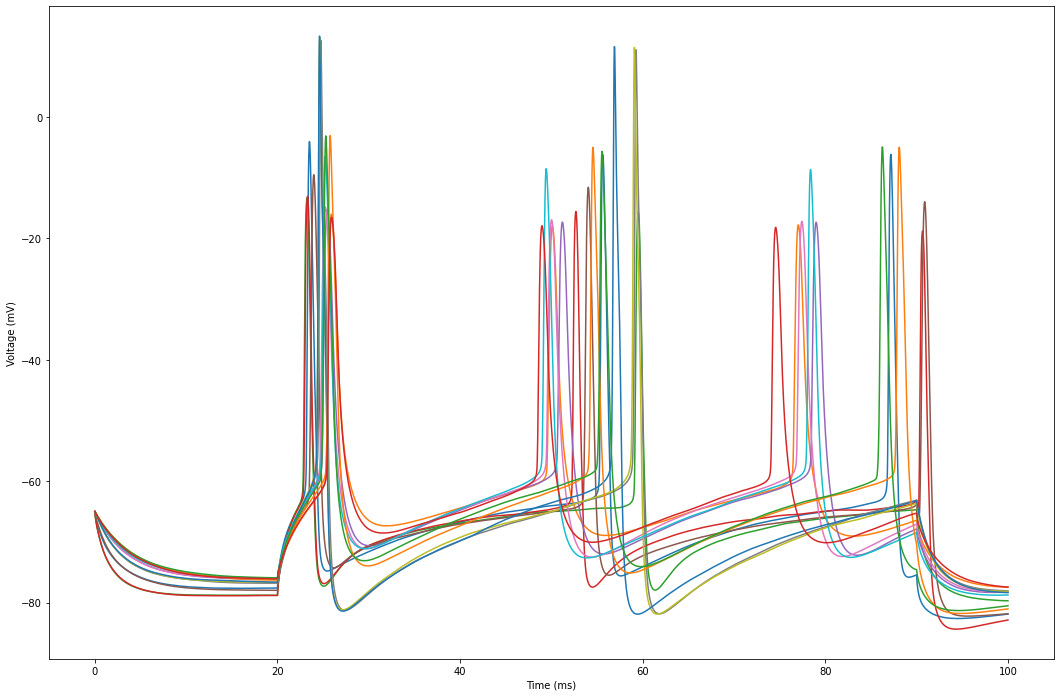
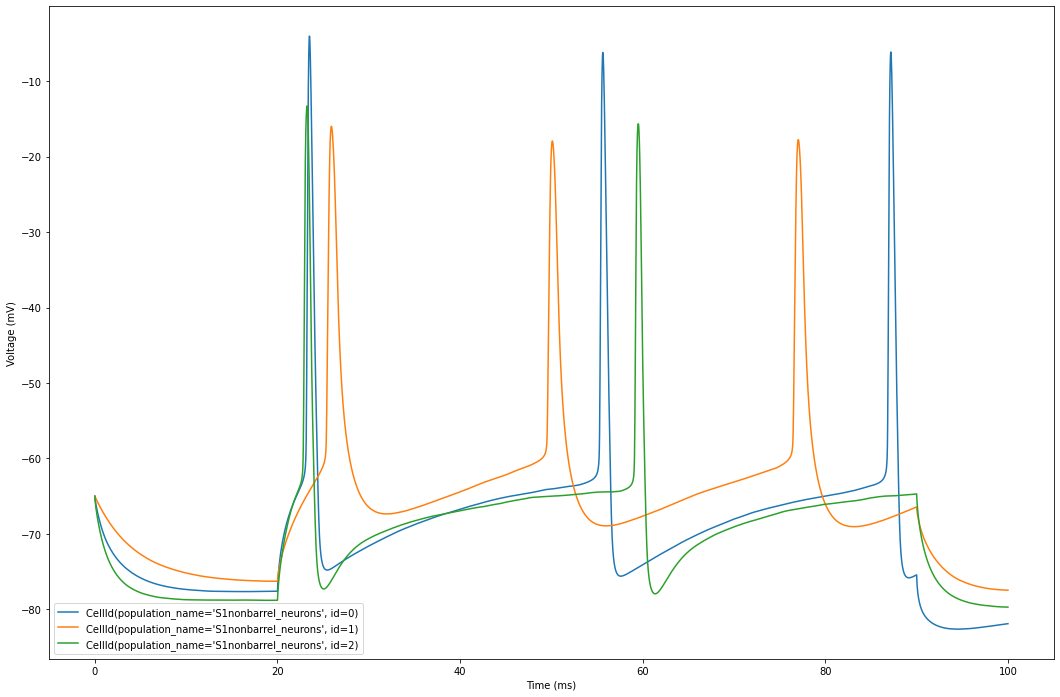
The plot displays the voltage traces simulated for each cell in our circuit.
plt.figure(figsize=(18, 12))
for cell_id in sim.cells:
time = sim.get_time_trace()
voltage = sim.get_voltage_trace(cell_id)
plt.plot(time, voltage, label=cell_id)
plt.xlabel("Time (ms)")
plt.ylabel("Voltage (mV)")
Let’s focus on 3 cells for better visualization
sim.cells = dict(list(sim.cells.items())[:3])
plt.figure(figsize=(18, 12))
for cell_id in sim.cells:
time = sim.get_time_trace()
voltage = sim.get_voltage_trace(cell_id)
plt.plot(time, voltage, label=cell_id)
plt.xlabel("Time (ms)")
plt.ylabel("Voltage (mV)")
plt.legend()
We are now ready to extract features. First, we will build the data structure for eFEL
traces = []
for cell_id in sim.cells:
voltage = sim.get_voltage_trace(cell_id)
trace = {}
trace['T'] = time
trace['V'] = voltage
trace['stim_start'] = [20]
trace['stim_end'] = [90]
traces.append(trace)
Next, we choose the specific features of interest
features = ['peak_time', 'AHP_time_from_peak', 'AP_height', 'AHP_depth_abs', 'all_ISI_values']
Finally, we perform the feature extraction
traces_results = efel.get_feature_values(traces, features)
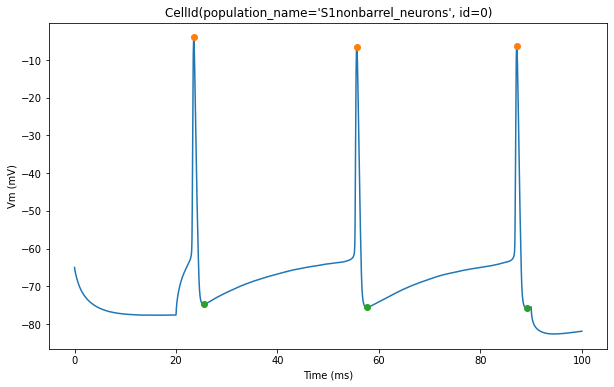
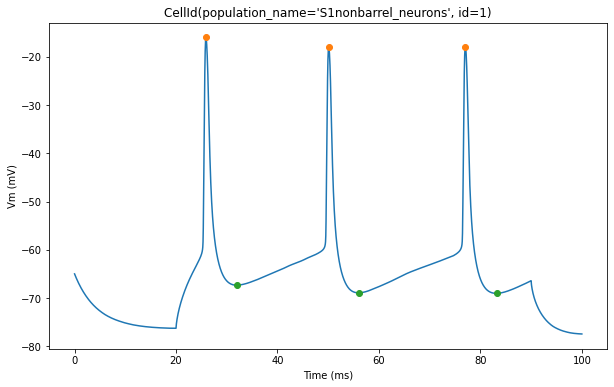
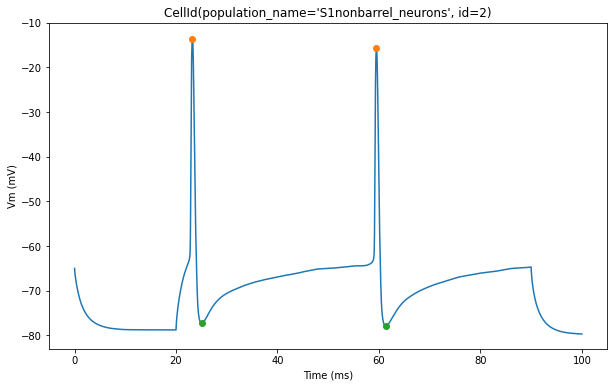
The plot below shows action potential (AP) height and depth of those 3 cells
import pylab
for trace, trace_result, cell_id in zip(traces, traces_results, sim.cells):
time = trace['T']
voltage = trace['V']
peak_times = trace_result['peak_time']
ahp_time = trace_result['AHP_time_from_peak']
ap_heights = trace_result['AP_height']
AHP_depth_abss = trace_result['AHP_depth_abs']
pylab.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
pylab.title(cell_id)
pylab.plot(time,voltage)
pylab.plot(peak_times, ap_heights, 'o')
pylab.plot(peak_times+ahp_time, AHP_depth_abss, 'o')
pylab.xlabel('Time (ms)')
pylab.ylabel('Vm (mV)')
pylab.show()
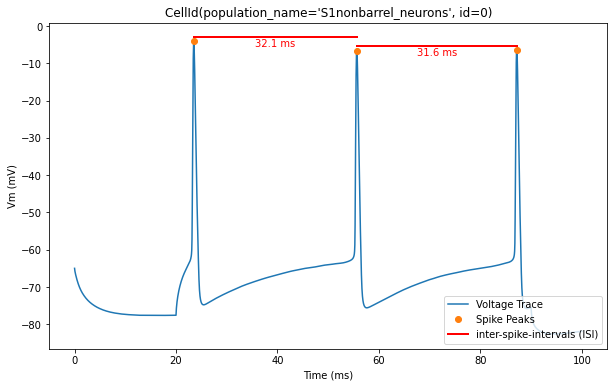
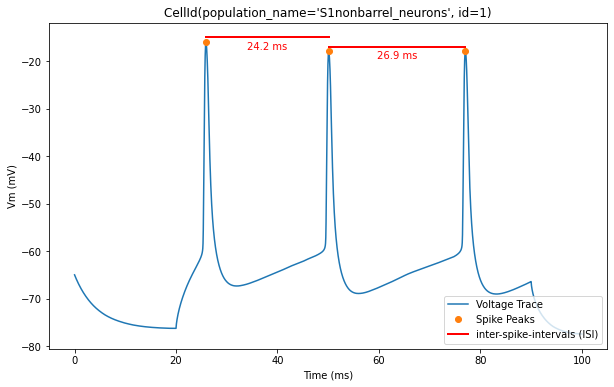
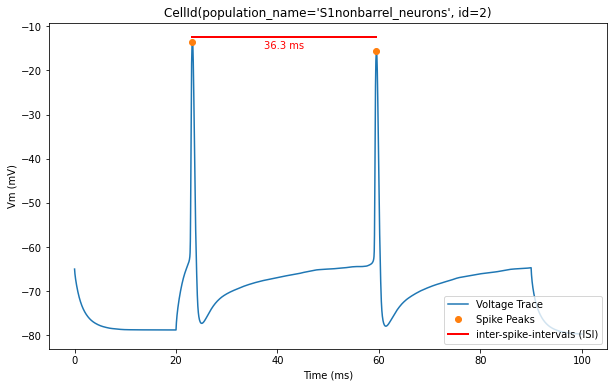
Now, let’s overlay the durations of the inter-spike intervals (ISIs) for a clearer visualization of the timing between spikes
for trace, trace_result, cell_id in zip(traces, traces_results, sim.cells):
time = trace['T']
voltage = trace['V']
peak_times = trace_result['peak_time']
ap_heights = trace_result['AP_height']
all_isi_values = trace_result['all_ISI_values']
pylab.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
pylab.title(cell_id)
pylab.plot(time, voltage, label='Voltage Trace')
pylab.plot(peak_times, ap_heights, 'o', label='Spike Peaks')
for i in range(len(peak_times) - 1):
start_spike_time = peak_times[i]
end_spike_time = peak_times[i + 1]
duration = round(all_isi_values[i], 2)
y_position = max(ap_heights[i], ap_heights[i + 1]) + 1
# Check if it's the first ISI line to be drawn and add a label, otherwise draw without a label
if i == 0:
pylab.plot([start_spike_time, end_spike_time], [y_position, y_position], 'r-', lw=2, label='inter-spike-intervals (ISI)')
else:
pylab.plot([start_spike_time, end_spike_time], [y_position, y_position], 'r-', lw=2)
# Adjust text position to be slightly lower
midpoint = (start_spike_time + end_spike_time) / 2
pylab.text(midpoint, y_position - 3, f'{duration} ms', verticalalignment='bottom', horizontalalignment='center', color='red')
pylab.xlabel('Time (ms)')
pylab.ylabel('Vm (mV)')
pylab.legend(loc='lower right')
pylab.show()